|
|
|
|
|
|
| Investigation of paper-based electronics continues to advance, showing exciting signs of progress. |
TSUKUBA, Japan, Sept 4, 2017 - (ACN Newswire) - Imagine folding up a paper-thin computer tablet like a newspaper. It sounds like something out of a science fiction movie, but such flexible electronics are moving closer to reality, according to a review in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
 | | Figure 1: Portable paper solar cells based on foldable, lightweight, transparent, conductive cellulose nanofiber paper. (Credit: CC-BY Macmillan Publishers Ltd) |
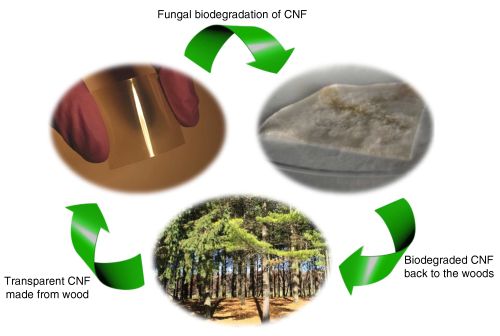 | | Figure 2: Cellulose, the building block of paper taken from plants, is an exciting alternative to the plastic, glass and silicon that currently make up most electronic devices. A key benefit is that it easily biodegrades in nature. (Credit: CC-BY Macmillan Publishers Ltd) |
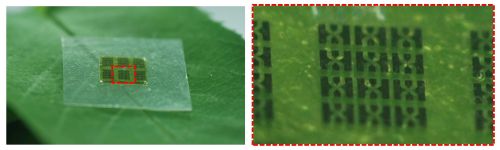 | | Figure 3: An array of heterojunction bipolar transistors on a cellulose nanofiber substrate put on a tree leaf. The right image shows the red-boxed area from the left image. (Credit: CC-BY Macmillan Publishers Ltd) |
Paper that is transparent and conducts electricity could have widespread applications, including foldable computers, transparent touch screens, and even digital camouflage clothing.
"With widespread and intensive efforts, low-cost and light-weight 'green' electronics fabricated on transparent nano paper substrate will provide new technologies impacting our daily life," state the review paper authors from Nanyang Technological University in Singapore.
Cellulose, the building block of paper taken from plants, is an exciting alternative to the plastic, glass and silicon that currently make up most electronic devices, including computers and mobile phones. Cellulose is renewable, biodegradable, strong, and lightweight. For the past 30 years, scientists have considered ways to combine these properties with electronics. Significant progress has been made in the past decade to manipulate the smallest plant fibers, called "nanocellulose", for use in electronics.
For example, researchers at Nanyang Technological University have made "nanopaper" out of nanocellulose and silver nanowires. It still conducted electricity after being folded in half 500 times. Some nanopapers have reached 90% transparency, while others are in the 80% range, similar to plastic. But, better than plastic, nanopapers degrade quickly. After metal electrodes are removed, nanopaper can be buried in soil and will fully degrade within a month. Researchers are still working on how to treat nanopapers that contain non-biodegradable materials, such as epoxy, to maintain their recyclability.
Many challenges remain before nanocellulose electronics become widespread. Currently, it is more expensive to produce pure nanopaper than glass or plastic. Cheaper preparation and fabrication methods are needed. Ideally, a common high-speed printing process used in electronic manufacturing called "roll to roll" can be adapted for nanocellulose. Also, the hydrophilic properties of cellulose make the items easy to degrade; this is desirable when it is time to dispose of them, but not during their operational life. The authors are optimistic that if these issues can be addressed, a wide range of electronics could soon be built from plants.
Article information:
Shaohui Li and Pooi See Lee
"Development and applications of transparent conductive nanocellulose paper"
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2017; 18:1, 620-633.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2017.1364976
For further information please contact:
Pooi See Lee,
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
pslee@ntu.edu.sg
Journal information
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials (STAM), http://www.tandfonline.com/stam is an international open access journal in materials science. The journal covers a broad spectrum of topics, including synthesis, processing, theoretical analysis and experimental characterization of materials. Emphasis is placed on the interdisciplinary nature of materials science and on issues at the forefront of the field, such as energy and environmental issues, as well as medical and bioengineering applications.
For more information about STAM please contact
Mikiko Tanifuji
Publishing Director
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
Tanifuji.Mikiko@nims.go.jp
Press release distributed by ResearchSEA for Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
Topic: Research and development
Source: Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
Sectors: Electronics, Materials & Nanotech, Science & Research
http://www.acnnewswire.com
From the Asia Corporate News Network
Copyright © 2026 ACN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Asia Corporate News Network.
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
| Science and Technology of Advanced Materials |
| July 8, 2025 06:48 HKT/SGT |
|
Progress towards potassium-ion batteries |
| June 23, 2025 00:15 HKT/SGT |
|
New method to blend functions for soft electronics |
| May 5, 2025 03:20 HKT/SGT |
|
New Database of Materials Accelerates Electronics Innovation |
| Jan 28, 2025 08:00 HKT/SGT |
|
High-brilliance radiation quickly finds the best composition for half-metal alloys |
| Dec 3, 2024 23:15 HKT/SGT |
|
Machine learning used to optimise polymer production |
| Oct 25, 2024 23:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Machine learning can predict the mechanical properties of polymers |
| July 30, 2024 20:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Dual-action therapy shows promise against aggressive oral cancer |
| Apr 17, 2024 22:00 HKT/SGT |
|
A new spin on materials analysis |
| Apr 12, 2024 18:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Kirigami hydrogels rise from cellulose film |
| Feb 27, 2024 08:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Sensing structure without touching |
| More news >> |
 |
|
|