|
|
|
|
|
|
| Scientists in Japan have combined two computational models to extract more data on steel alloys from a single test, with implications for the discovery of new materials. |
TSUKUBA, Japan, Nov 7, 2022 - (ACN Newswire) - A new approach uses data from one type of test on small metal alloy samples to extract enough information for building databases that can be used to predict the properties and potentials of new materials. The details were published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials: Methods.
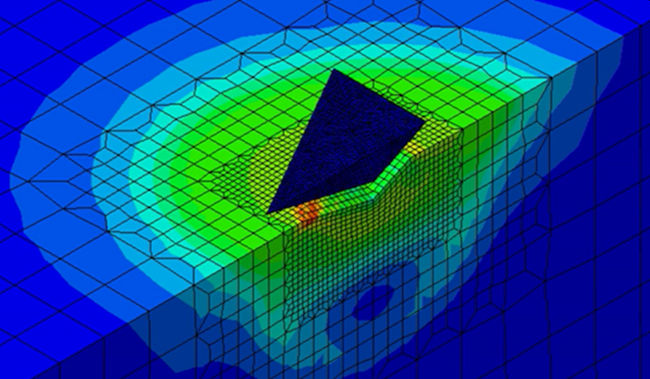 | | The scientists used computer simulations to build database of material properties. |
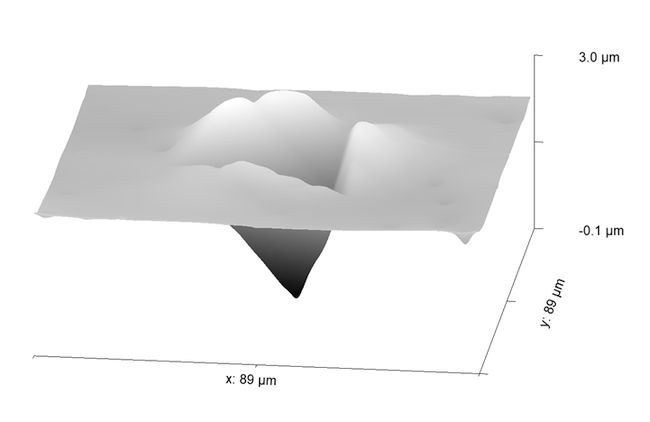 | | The Scientists found a way to use topography around indentation impression to predict other properties measured by a tensile or compression test. |
The test is called instrumented indentation. It involves driving an indenter tip into a material to probe some of its properties, such as hardness and elastic stiffness. Scientists have been using the data extracted from instrumented indentation to estimate the stress-strain curve of materials using computational simulations. This curve, and the data it provides, is important for understanding a material's properties. That data is also used for building massive materials databases, which can be used, in conjunction with artificial intelligence, for predicting new materials.
A problem scientists face is that this approach for estimating material properties is limited when it comes to materials called 'high work-hardening alloys': metal alloys, like steel, that are strengthened through physical processes like rolling and forging. Only so much information can be estimated from the curve of these materials. To get the necessary additional information needed to determine their properties, more experiments would need to be done, which costs time, effort and money.
Ta-Te Chen of the University of Tsukuba and Ikumu Watanabe of the National Institute for Materials Science in Japan have developed a new computational approach to extract that additional information from instrumented indentation tests on work-hardening alloys.
"Our approach builds on an already-existing model, making it ready for use in industry. It is also applicable to existing data, including hardness," says Watanabe.
The approach involves combining the results from two computational models, the power-law and linear hardening models, which produce their own individual stress-plastic strain curves from information gathered from indentation tests. Combining the data from both curves provides the extra data that, when added to the original stress-strain curve, shows a more holistic picture of the work-hardening alloys' properties.
The scientists validated their approach by using it on a high-work-hardening stainless steel.
We have extended this approach to also evaluate mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, which can contribute to the development of high-temperature alloys," says Chen.
Further information
Ikumu Watanabe
National Institute for Materials Science
Email: WATANABE.Ikumu@nims.go.jp
About Science and Technology of Advanced Materials: Methods (STAM Methods)
STAM Methods is an open access sister journal of Science and Technology of Advanced Materials (STAM), and focuses on emergent methods and tools for improving and/or accelerating materials developments, such as methodology, apparatus, instrumentation, modeling, high-through put data collection, materials/process informatics, databases, and programming. https://www.tandfonline.com/STAM-M
Dr. Yasufumi Nakamichi
STAM Methods Publishing Director
Email: NAKAMICHI.Yasufumi@nims.go.jp
Press release distributed by Asia Research News for Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
Topic: Press release summary
Source: Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
Sectors: Electronics, Materials & Nanotech, Science & Research
http://www.acnnewswire.com
From the Asia Corporate News Network
Copyright © 2026 ACN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Asia Corporate News Network.
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
| Science and Technology of Advanced Materials |
| July 8, 2025 06:48 HKT/SGT |
|
Progress towards potassium-ion batteries |
| June 23, 2025 00:15 HKT/SGT |
|
New method to blend functions for soft electronics |
| May 5, 2025 03:20 HKT/SGT |
|
New Database of Materials Accelerates Electronics Innovation |
| Jan 28, 2025 08:00 HKT/SGT |
|
High-brilliance radiation quickly finds the best composition for half-metal alloys |
| Dec 3, 2024 23:15 HKT/SGT |
|
Machine learning used to optimise polymer production |
| Oct 25, 2024 23:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Machine learning can predict the mechanical properties of polymers |
| July 30, 2024 20:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Dual-action therapy shows promise against aggressive oral cancer |
| Apr 17, 2024 22:00 HKT/SGT |
|
A new spin on materials analysis |
| Apr 12, 2024 18:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Kirigami hydrogels rise from cellulose film |
| Feb 27, 2024 08:00 HKT/SGT |
|
Sensing structure without touching |
| More news >> |
 |
|
|